 LinuxBlog.xyz
LinuxBlog.xyz January 6, 2021 - Patrick Kerwood
Installing Cert Manager with Helm 3
Here's a quick how-to on installing Cert Manager in your Kubernetes cluster and setting up Issuers with Let's Encrypt HTTP and DNS validation. With Helm 3 the installation process is a breeze.
# Prerequisites
A prerequisite for installing Cert Manager with Helm is of course Helm. Go to the Helm install docs (opens new window) and get a piece of that cake.
Efter installing Helm, add the Jetstack repo and update your Helm repositories.
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo update
# Installing Cert Manager
Create a namespace for Cert Manager.
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
Before installing, go to the install docs (opens new window), verify the latest version and replace it in the example below.
helm install \
cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--version v1.6 \
--set installCRDs=true
That's it! Cert Manager is installed.
# Adding a Let's Encrypt HTTP-01 Issuer
Below is is an example of a ClusterIssuer, named le-http01, that uses HTTP-01 validation. This is the easiest method because there's no more configuration than below manifest. The only drawback is that your cluster has to be accessible from the internet, for Let's Encrypt to validate the domain name.
Change the email property, save below yaml to a file and apply it to your cluster.
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: le-http01
spec:
acme:
email: your-email@example.org
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
privateKeySecretRef:
name: le-http01-account-key
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
# Adding a Let's Encrypt DNS-01 Issuer
When using the DNS validation, you can request certificates from a cluster that's not accessible from the internet, via a DNS providers API. You can find a list of supported providers here. (opens new window)
In this example I will be using Cloudflare as the DNS provider.
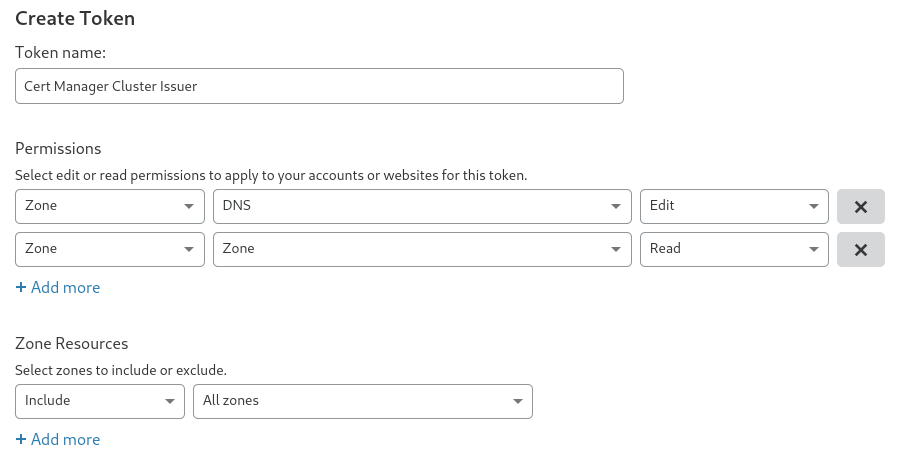
Login to your Cloudflare account, go to "My Profile" -> "API Tokens" and create a token with the following permissions.
- Permissions:
- Zone - DNS - Edit
- Zone - Zone - Read
- Zone Resources:
- Include - All Zones.
If you want you can lock the token down for a specific zone.
Create a secret with the Cloudflare token.
kubectl create secret generic cloudflare-api-token --from-literal=api-token=<insert-token-here> -n cert-manager
Change the email property, save below yaml to a file and apply it to your cluster.
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: le-dns01
spec:
acme:
email: your-email@example.org
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
privateKeySecretRef:
name: le-dns01-account-key
solvers:
- dns01:
cloudflare:
apiTokenSecretRef:
name: cloudflare-api-token
key: api-token
# Ingress Example
Below is an example of an ingress definition with TLS enabled, using the le-http01 cluster issuer.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: hello-world
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: le-http01
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- hello.example.org
secretName: hello-le-secret
rules:
- host: hello.example.org
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: hello-world
servicePort: 80